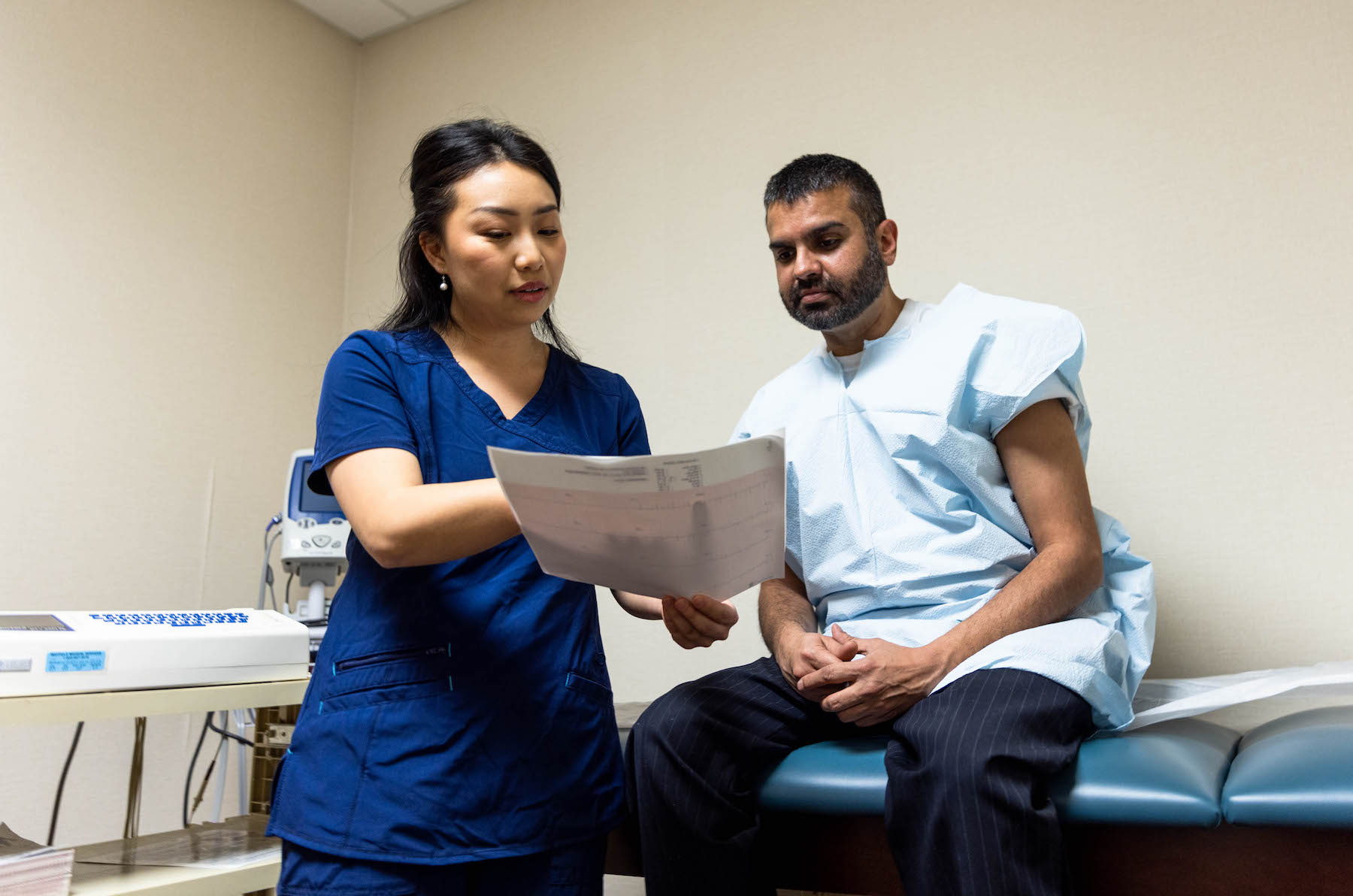
What is Hepatocellular Carcinoma?
Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) is the most common type of primary liver cancer. It occurs most often as a result of chronic liver disease such as hepatitis C, hepatitis B, and NASH. Most people do not have signs or symptoms during the early stages but may develop symptoms as the disease progresses. HCC is diagnosed using a variety of tests including blood tests, imaging, and through a biopsy, a procedure to remove a sample of the liver tissue.
There are several FDA approved treatments and over the counter medications available to help patients manage the symptoms. While many effective treatments are available, clinical trials may still be your best option as they are working to develop more advanced therapies.
Risk Factors
- Chronic Liver Diseases
- Hepatitis B or C
- Alcohol Consumption
Signs & Symptoms
-
- Weight Loss
- Loss of Appetite
- Abdominal Pain
- Nausea or Vomiting
- General Weakness / Fatigue
- Abdominal Swelling
- Jaundice
- White, Chalky Stools
Treatments
-
- Surgery
- Chemotherapy
- Radiation
- Targeted Therapy
- Immunotherapy
- Supportive (palliative) Care

Managing Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Working with your healthcare provider to determine the stage of cancer is key in creating a path for treatment of your liver cancer. There are several treatment options available to patients depending on the stage of disease.
Your healthcare provider will be able to inform you of the treatment options available to you that will give you the best chance in making an informed decision on your treatment path. Treatment options may include surgery to remove the tumor, liver transplant, radiation, immunotherapy, chemotherapy, and supportive (palliative) care. Clinical trials may also be an option for you as they provide opportunities for alternative treatments.
Be sure to discuss all of your options with your healthcare provider.

FAQs about Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Frequently Asked Questions
How is HCC diagnosed?
Only about 25% of patients who do not have a history of liver disease are diagnosed with HCC. Depending on your risk factors, family history, and any existing liver damage or disease, your provider may order routine lab work to monitor for Alpha Fetoprotein (AFP, a liver enzyme) levels. If elevated, your provider will order imaging to search for lesions in the liver. If a lesion is identified, it can be biopsied to screen for cancer. This is a common screening undergone by most level 4 (NASH or cirrhosis) patients.
I’ve been diagnosed with HCC. What’s my prognosis?
The prognosis you receive after you have been diagnosed with HCC will highly depend on your medical history and your options for treatment. But primarily, prognoses are made based on the stage in which the HCC has developed and/or where the HCC has spread.
How do I treat HCC?
Like other cancers, HCC can be treated using a variety of methods such as surgery, chemotherapy, radiation, and more. Clinical trials also offer patients the opportunity to try new treatments for liver cancer. If you have any questions or are interested in getting started, KCRI can help you determine your candidacy for an HCC clinical trial!
Don't see the study you're looking for?
Those that Participate:
- See a board-certified physician at no cost
- Have access to possible new treatment options before the general public
- May be compensated for time and travel
We are continually getting new research studies for all types of conditions. Submit your information today to be contacted for upcoming research opportunities.